By: AnaLeite 1,2, Rubén Domínguez 3 , Lia Vasconcelos 1, Iasmin Ferreira 1 , Etelvina Pereira 1, Victor Pinheiro 4 Divanildo Outor-Monteiro 4, Sandra Rodrigues 1 , José Manuel Lorenzo 2,3 Silvina Cecilia Andrés 6 , Paulo C. B. Campagnol 7 , Eva María Santos 5 , and Alfredo Teixeira 1,*
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Diets
2.2. Slaughter Procedure
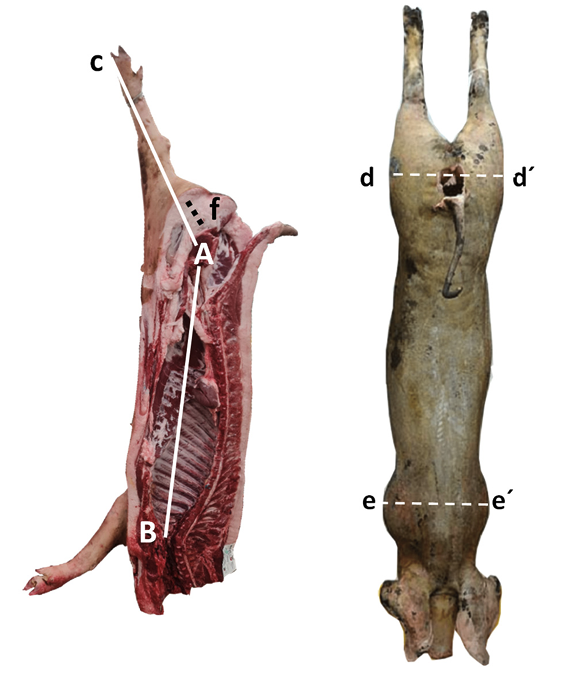
2.3. Carcass Quality Measurements
2.4. Physicochemical Analysis of Meat and Fat
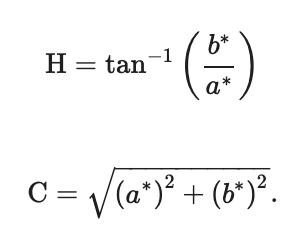

2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
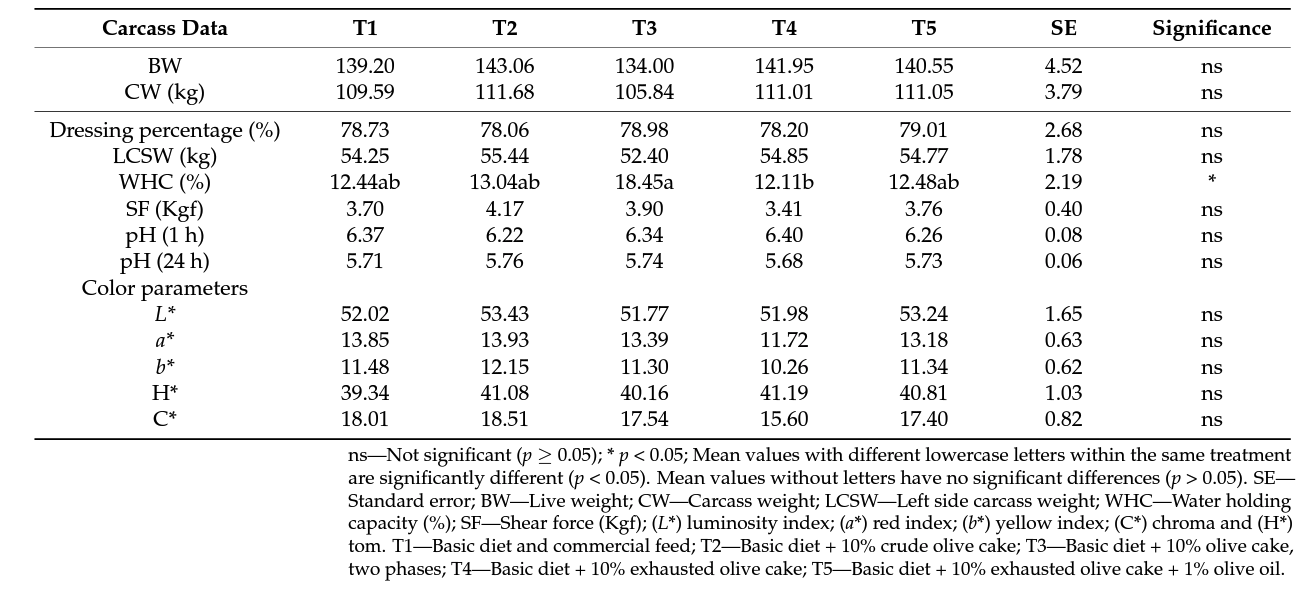
3.1. Carcass Evaluation
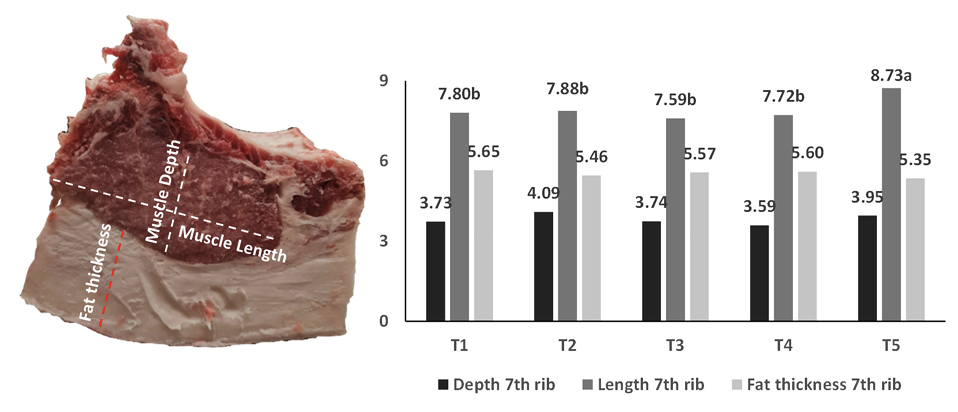
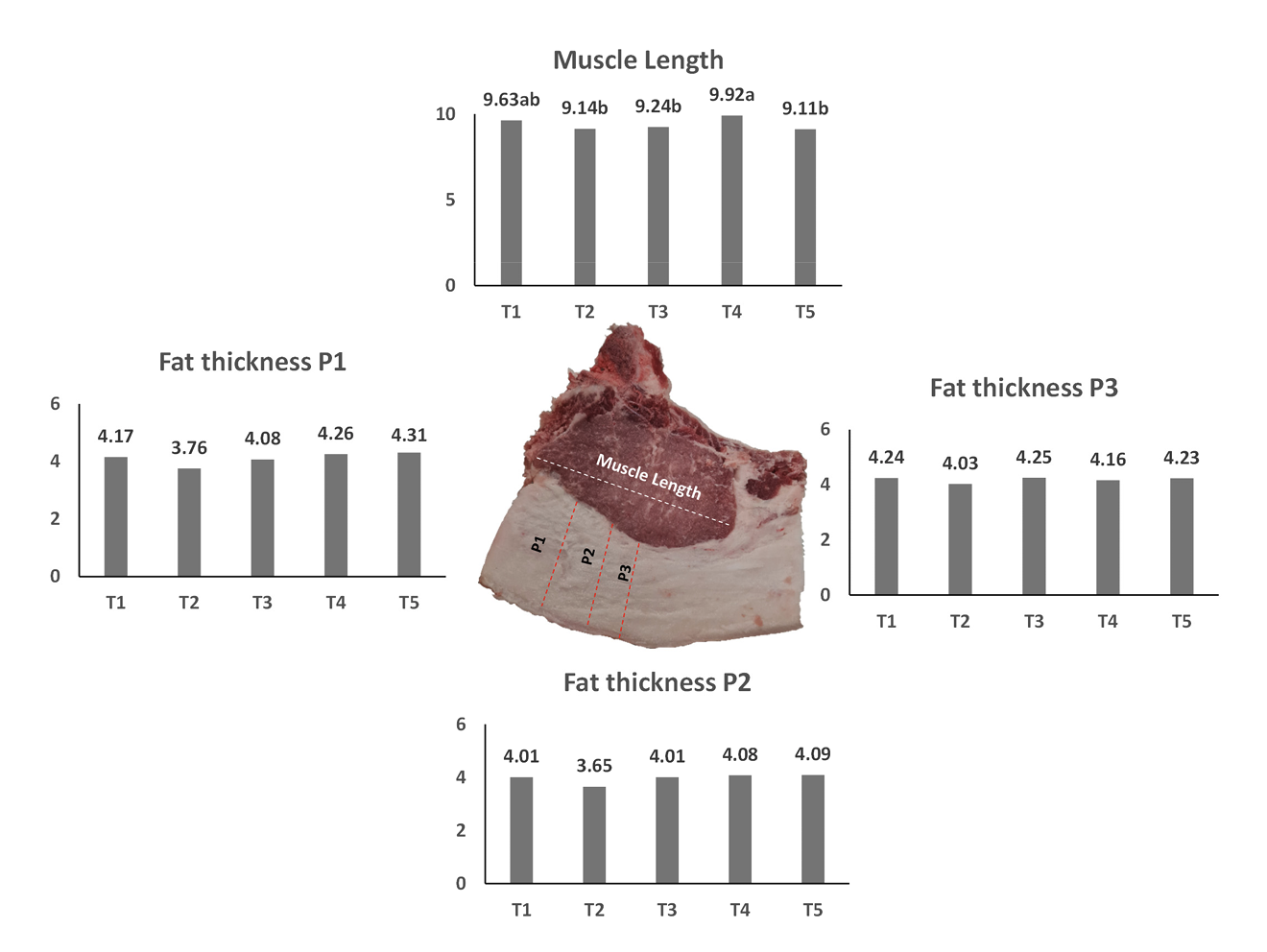
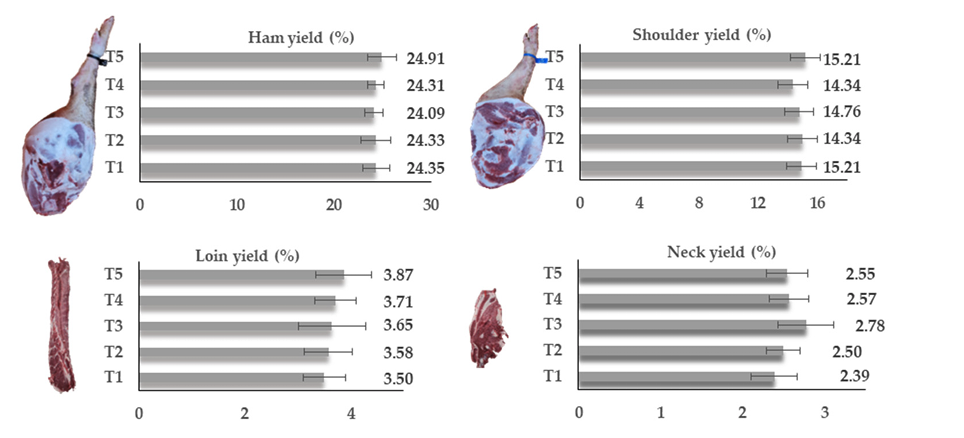
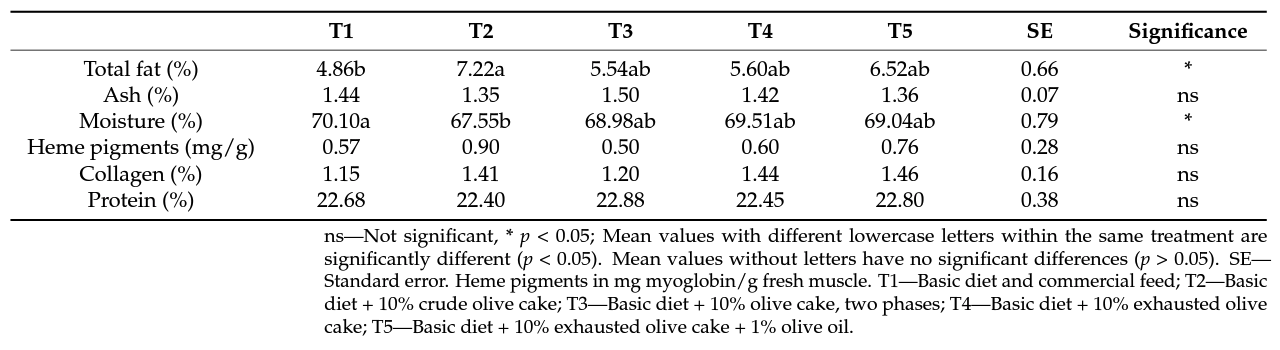
3.2. Chemical Composition
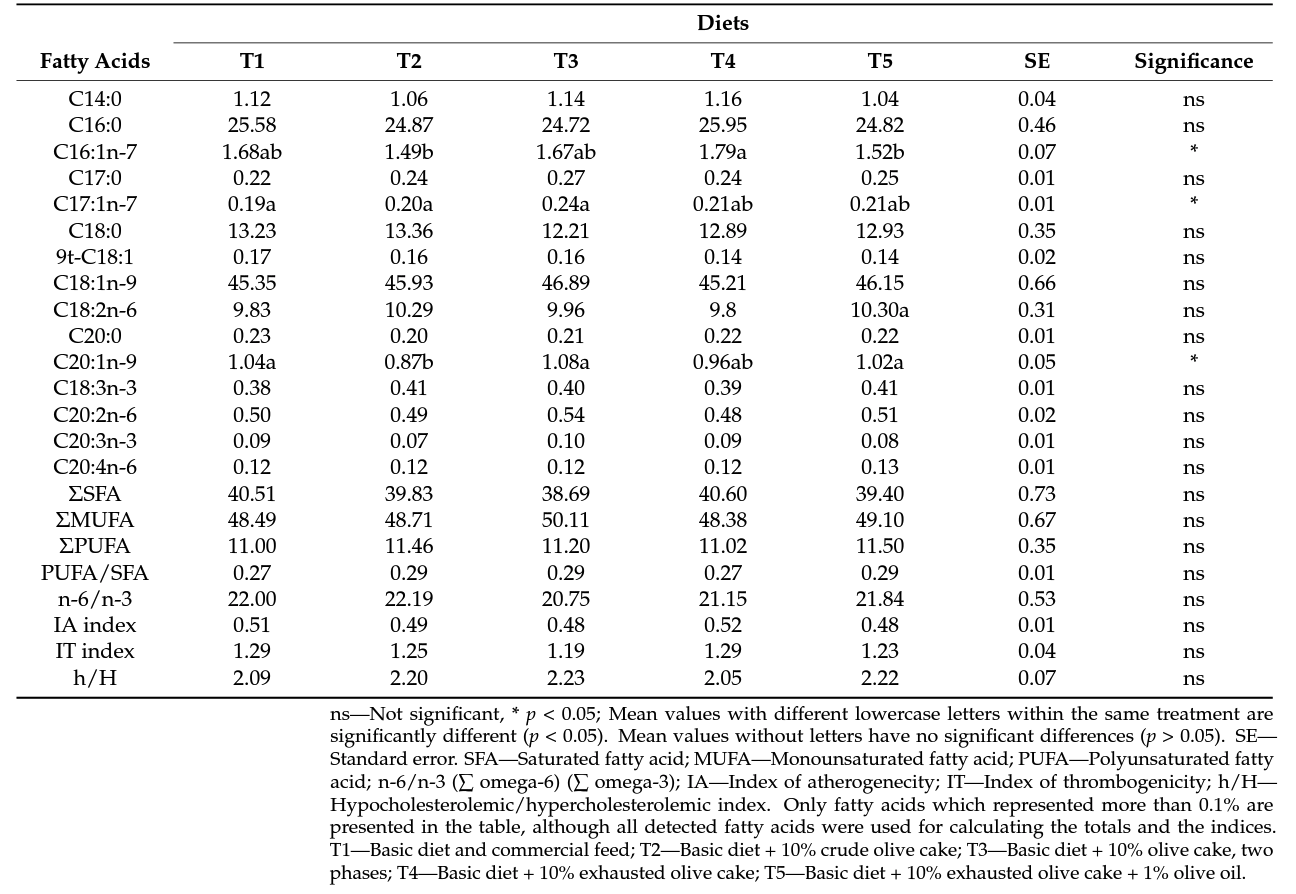
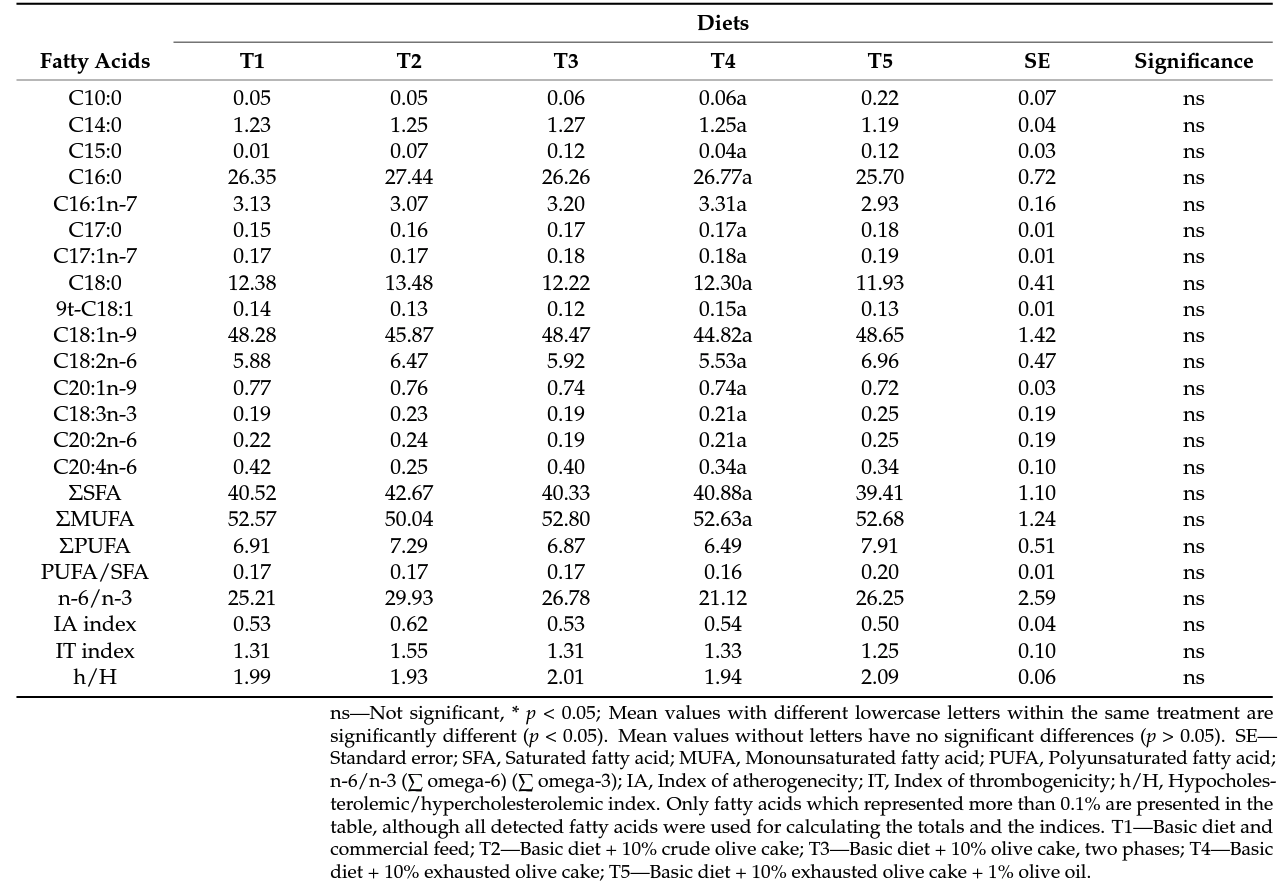
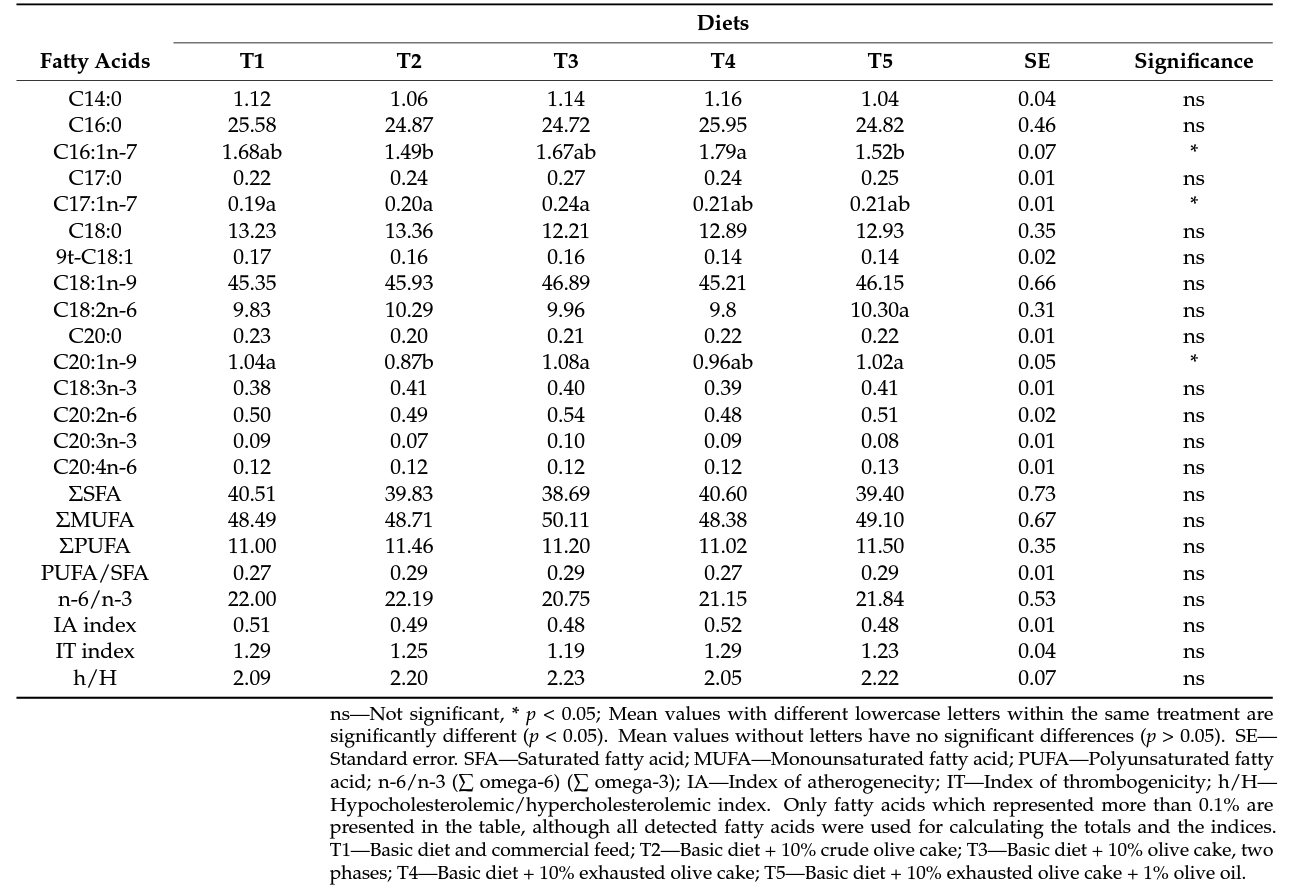
3.3. Fatty Acid Profile and Lipidic Quality
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Molina-Alcaide, E.; Yáñez-Ruiz, D.R. Potential use of olive by-products in ruminant feeding: A review. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2008, 147, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Casa, J.A.; Bueno, J.S.; Castro, E. Recycling of residues from the olive cultivation and olive oil production process for manufacturing of ceramic materials. A comprehensive review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 296, 126436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Barral-Martinez, M.; Chamorro, F.; Echave, J.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; et al. Applications of by-products from the olive oil processing: Revalorization strategies based on target molecules and green extraction technologies. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2021, 116, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, P.; Gullón, B.; Astray, G.; Carpena, M.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Prieto, M.A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Valorization of by-products from olive oil industry and added-value applications for innovative functional foods. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liotta, L.; Chiofalo, V.; Presti, L.V.; Chiofalo, B. In vivo performances, carcass traits, and meat quality of pigs fed olive cake processing waste. Animals 2019, 9, 1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrer, P.; Calvet, S.; García-Rebollar, P.; Blas, C.; Jiménez-Belenguer, A.I.; Hernández, P.; Piquer, O.; Cerisuelo, A. Partially defatted olive cake in finishing pig diets: Implications on performance, faecal microbiota, carcass quality, slurry composition and gas emission. Animal 2020, 14, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gálvez-Pérez, A.; Martín-Lara, M.A.; Calero, M.; Pérez, A.; Canu, P.; Blázquez, G. Experimental investigation on the air gasification of olive cake at low temperatures. Fuel Process. Technol. 2021, 213, 103703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufariello, M.; Durante, M.; Veneziani, G.; Taticchi, A.; Servili, M.; Bleve, G.; Mita, G. Patè Olive cake: Possible Exploitation of a by-product for food applications. Front. Nutr. 2019, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Pimentel, F.B.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. Olive by-products: Challenge application in cosmetic industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 70, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzamaloukas, O.; Neofytou, M.C.; Simitzis, P.E. Application of olive by-products in livestock with emphasis on small ruminants: Implications on rumen function, growth performance, milk and meat quality. Animals 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Otmani, S.; Chebli, Y.; Hornick, J.L.; Cabaraux, J.F.; Chentouf, M. Growth performance, carcass characteristics and meat quality of male goat kids supplemented by alternative feed resources: Olive cake and cactus cladodes. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2021, 272, 114746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durante, M.; Ferramosca, A.; Treppiccione, L.; Di Giacomo, M.; Zara, V.; Montefusco, A.; Piro, G.; Mita, G.; Bergamo, P.; Lenucci, M.S. Application of response surface methodology 8RSM) for the optimization of supercritical CO2 extraction of oil from pate cake: Yield, content of bioactive molecules and biological effects in vivo. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127405–127410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joven, M.; Pintos, E.; Latorre, M.A.; Suárez-Belloch, J.; Guada, J.A.; Fondevilla, M. Effect of replacing barley by increasing levels of olive cake in the diet of finishing pigs: Growth performances, digestibility, carcass, meat and fat quality. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2014, 197, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiofalo, B.; Liotta, L.; Zumbo, A.; Chiofalo, V. Administration of olive cake for ewe feeding effect on milk yield and composition. Small Rumi. Res. 2004, 55, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resolução da Assembleia da República nº 279/2018. Available online: https://dre.pt/dre/detalhe/resolucao-assembleia-republica/279-2018-116154041 (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- García-Casco, J.M.; Muñoz, M.; Martínez-Torres, J.M.; López-García, A.; Fernández-Barroso, M.A.; González-Sánchez, E. Alternative Feeding in Iberian Pigs during Growth period: Incorporation of Olive Cake in a dry or wet (silage) form. Agric. Conspec. Sci. 2017, 82, 147–150. [Google Scholar]
- Panouillé, M.; Ralet, M.C.; Bonnim, E.; Thibault, J.F. Recovery and reuse of trimmings and pulps from fruit and vegetable processing. In Handbook of Waste Management and Co-Product Recovery in Food Processing; Waldron, K., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2007; Volume 1, pp. 417–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Journal of the European Union. Official Journal of the European Union Council Regulation (EC) No 510/2006 ‘Carne de Bísaro Transmontano’ or ‘Carne de Porco Transmontano’ No: EC PT/PDO/005/0457/20.04.2005 C89 24.04.2007. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/PT/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R0510&from=IT (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Hernández-Matamoros, A.; Paniagua, B.M.; Izquierdo, C.M.; Tejeda, S.J.; González-Sanchez, E. Use of olive cake and tomate peel in the Iberian pig feed. In Proceedings of the XIV Jornadas sobre Producción Animal, Zaragoza, Spain, 17–18 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, J.; Teixeira, A. Slaughter weight rather than sex affects carcass cuts and tissue composition of Bísaro pigs. Meat Sci. 2019, 154, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Regulation (EC). No. 1099/2009 on the Protection of Animals at the Time of Killing. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02009R1099-20180518 (accessed on 11 April 2022).
- Sánchez-Macias, D.; Castro, N.; Rivero, M.A.; Argüello, A.; Morales-de la Nuez, A. Proposal for standard methods and procedure for guinea pig carcass evaluation, jointing and tissue separation. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2015, 44, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Teixeira, A.; Silva, S.R.; Hasse, M.; Almeida, J.M.H.; Dias, L. Intramuscular fat prediction using color and image analysis of Bísaro pork breed. Foods 2021, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP-ISO-3441/2008; Determinação do pH (Método de Referência). Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 2008.
- AOAC International; Cunniff, P. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis of AOAC International, 16th ed.; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 1995; ISBN 9780935584547. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira, A.; Domínguez, R.; Rey, J.F.; Aleu, G.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M. pH and Color. In Methods to Assess the Quality of Meat Products; Lorenzo, J.M., Domínguez, R., Pateiro, M., Munekata, P.E., Eds.; Methods and Protocols in Food Science; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP-ISO-1614/2002; Determination of Moisture Content. Reference Method (ISO 1442:1197). Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy, and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 2002.
- NP-ISO-1615/2002; Determination of Total Ashes. Reference Method. Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy, and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 2002.
- NP-ISO-1612/2002; Determination of TOTAL nitrogen Content. Reference Method (ISO 937:1978). Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy, and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 2002.
- Honikel, K.O. Reference methods for the assessment of physical characteristics of meat. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echegaray, N.; Rosmini, M.; Pateiro, M.; Domínguez, R.; Munekata, P.E.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Santos, E.M.; Bermúndez, R. Texture Analysis. In Methods to Assess the Quality of Meat Products; Lorenzo, J.M., Domínguez, R., Pateiro, M., Munekata, P.E., Eds.; Methods and Protocols in Food Science; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- NP-ISO-1987/2002; Determination of Hydroxyproline Content. Reference Method (ISO 3496:1994). Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy, and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 2002.
- Hornsey, H.C. The colour of cooked cured pork. I-Estimation of the nitric oxide-haem pigments. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1956, 7, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Stanley, G.H.S. A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, R.; Borrajo, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. The effect of cooking methods on nutritional value of foal meat. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulbricht, T.L.V.; Southgate, D.A.T. Coronary heart disease: Seven dietary factors. Lancet 1991, 338, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, A.B.; Neves, J.; Charneca, R.; Tirapicos, N.J.; Martins, J.M. Influence of slaughter weight on growth and carcass characteristics of Alentejano pigs. Options Méditerr. 2007, 76, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, J.M.; Fialho, R.; Alburquerque, A.; Neves, J.; Freitas, A.; Nunes, J.T.; Charneca, R. Growth, blood, carcass and meat quality traits from local pig breeds and their crosses. Animal 2020, 14, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, D.; Vazquez, J.A.; Lorenzo, J.M. Growth performance, carcass and meat quality of the Celta pig crossbred with Duroc and Landrace genotypes. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glinoubol, J.; Jaturasitha, S.; Mahinchaib, P.; Wicke, M.; Kreuzer, M. Effects of crossbreeding Thai Native or Duroc pigs with Pietrain pigs on Carcass and Meat quality. Agric. Agricult. Sci. 2015, 5, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Parunovic, N.; Dordevic, V.; Radovic, C.; Savic, R.; Karabasil, N.; Trbovic, D.; Ciric, J. Effect of rearing system on carcass properties, chemical content and fatty acid composition of backfat from Mangalitsa pigs. J. Meat Technol. 2020, 61, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.S.; Shi, L.; Gao, R.; Su, B.C.; Wang, H.; Shi, B.M.; Shan, A.S. Effects of conjugated linoleic acid or betaine on the growth performances and fatty acid composition in backfat and belly fat of finishing pigs fed dried distillers grains with soluble. Animals 2015, 9, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Malgwi, I.H.; Giannuzzi, D.; Gallo, L.; Halas, V.; Carnier, P.; Schiavon, S. Influence of slaughter weight and sex on growth performance, carcass characteristics and Ham traits of Heavy pigs fed ad-libitum. Animals 2022, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NP-ISO-2931/1987; Suínos abatidos para consume direto. -Corte da meia carcaça. Portuguese Institute of Quality, Ministry of Economy, and Innovation: Caparica, Portugal, 1987.
- Echegaray, N.; Domínguez, R.; Franco, D.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Carballo, J. Effect of the use of chestnuts (Castanea sativa Miller) in the finishing diet of Celta pig breed on the shelf-life of meat refrigerated and frozen. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, A.; Oliveira, A.; Amorim, A.; Gonçalves, A.; Paulos, K.; Pereira, E.; Rodrigues, S.; Teixeira, A. Qualidade da Carne. In Boom Porco Bísaro—Qualidade da Carcaça, 1st ed.; Fernandes, A., Teixeira, A., Eds.; Quinta do Bísaro: Bragança, Portugal, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 82–96. [Google Scholar]
- Franco, D.; Bragado, C.; Lorenzo, J.M. Características de la canal de cerdo Celta. In Book Manual dele Cerdo Celta, 1st ed; Lorenzo, J.M., Rodríguez, M., Eds.; CETECA: Galícia, Spain, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Fernández, J. La recuperación del Gochu Asturcelta. In Book Manual del Gochu Asturcelta, 1st ed.; Samalea, A., Ed.; Serida: Asturias, Spain, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, K. Drip loss in pork: Influencing factors and relation to further meat quality traits, A review. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2007, 124, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boler, D.D. Species of meat animals. In Encyclopedia of Meat Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloveras, M.R.; Goenaga, P.R.; Irurueta, M.; Carduza, F.; Grigioni, G.; García, P.T.; Améndola, A. Meat quality traits of commercial hybrid pigs in Argentina. Meat Sci. 2008, 79, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Castiñeiras, B.D.; Franco, I.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Carballo, J. Características de la carne y de la grasa del Cerdo de Raza Celta. In Book Manual del Cerdo Celta, 1st ed.; Lorenzo, J.M., Rodríguez, M., Eds.; CETECA: Galícia, Spain, 2012; Volume 1, pp. 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Mancini, R.; Hunt, M.C. Current research in meat color. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 100–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Mourvaki, E.; Cardinali, R.; Servili, M.; Sebastiani, B.; Ruggeri, S.; Mattioli, S.; Taticchi, A.; Esposto, S.; Castellini, C. Effect of dietary supplementation with olive pomaces on the performances and meat quality of growing rabbits. Meat Sci. 2012, 92, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlisin, P.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, S.K. Effects of crossbreeding and gender on the carcass traits and meat quality of Korean native Black pig and Duroc Crossbred. Aslan Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Van der Wal, P.G.; Bolink, A.H.; Merkus, G.S.M. Differences in quality characteristics of normal, PSE and DFD pork. Meat Sci. 1988, 24, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Rodrigues, S. Pork meat quality of Preto Alentejano and Commercial Largewhite Landrace Cross. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusec, G.; Komlenic, M.; Gvozdanovic, K.; Sili, V.; Kravavica, M.; Radisic, Z.; Kusec, I.D. Carcass Composition and Phisicochemical characteristics of meat from Pork Chains Based on Native and Hybrid Pigs. Animals 2022, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, M.S.; Lopes, P.A.; Costa, P.; Coelho, D.; Alfaia, C.M.; Prates, J.A.M. Reducing protein diets increase intramuscular fat of psoas major, a red muscle, in lean and fatty pig genotypes. Animals 2017, 11, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, M.P.; Valencia, D.G.; Nieto, M.; Lázaro, R.; Mateos, G.G. Influence of sex and terminal sire line on performance and carcass and meat quality of Iberian pigs reared under intensive production systems. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, I.; Escamilla, M.C.; García, J.; García-Fontán, M.C.; Carballo, J. Fatty acid profile of the fat from Celta pig breed fattened using a traditional feed: Effect of the location I the carcass. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2006, 19, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortina, R.; Barbera, S.; Lussiana, C.; Mimosi, A.; Tassone, S.; Rossi, A.; Zanardi, E. Performances and meat quality of two Italian pig breeds fed diets for commercial hybrids. Meat Sci. 2005, 71, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zumbo, A.; Sutera, A.M.; Tardiolo, G.; D’Alessandro, E. Sicilian Black pig: Ana overview. Animals 2020, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wentao, C.; Xie, J.; Zhu, X.; Shan, T. Low Dietary n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio regulates meat quality, reduces triglycerides content, and improves fatty acid composition of meat in Heigai Pigs. Animals 2020, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Wu, X.; Xie, C.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, B. Meat Quality and fatty acid profiles of Chinese Ningxiang pigs following supplementation with N-Carbamyglutamate. Animals 2020, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Stasiak, K.; Roslewska, A.; Stanek, M.; Jankowiak, H.; Cygan-Szczegielniak, D.; Bocian, M. Comparison of the fatty acid profile in the meat of pigs and wild boars. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2018, 30, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuernberg, K.; Fischer, K.; Nuernberg, G.; Kuechenmeister, U.; Klosowska, D.; Eliminowska-Wenda, G.; Fiedler, I.; Ender, K. Effects of dietary olive and linseed oil on lipid composition, meat quality, sensory characteristics and muscle structure in pigs. Meat Sci. 2005, 70, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevrkla, P.; Kapelanski, W.; Václavkova, E.; Hadas, Z.; Cebulska, A.; Horky, P. Meat quality and fatty acid profile of pork and black indigenous breed and a commercial hybrid of pigs. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2017, 17, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- British Department of Health. Nutritional aspects of cardiovascular disease. Report of the Cardiovascular Review group Committee on Medical Aspects of Food Policy. Rep. Health Soc. Subj. 1994, 46, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Chiofalo, B.; Lo Presti, V.; Piccolo, D.; Arena, G. Nero Siciliano pig Effect of the diet on meat quality. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2007, 6, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional Indices for Assessing Fatty acids: A Mini-Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cava, R.; Estévez, M.; Ruiz, J.; Morcuende, D. Physicochemical characteristics of three muscles from free-range reared Iberian pigs slaughtered at 90 kg live weight. Meat Sci. 2003, 63, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woloszyn, J.; Haraf, G.; Okruszek, A.; Werenska, M.; Goluch, A.; Teleszko, M. Fatty acid profiles and health lipid indices in the breast muscles of local Polish goose varieties. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, J.M.; Montes, R.; Purrinos, L.; Cobas, N.; Franco, D. Fatty acid composition of Celta pig breed as influenced by sex and location of fat in the carcass. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



